通过iperf3测速,测试你与vps之间的真实速度
Iperf3 是一个网络性能测试工具。Iperf可以测试最大TCP和UDP带宽性能,具有多种参数和UDP特性,可以根据需要调整,可以报告带宽、延迟抖动和数据包丢失.对于每个测试,它都会报告带宽,丢包和其他参数,可在Windows、Mac OS X、Linux、FreeBSD等各种平台使用,是一个简单又实用的小工具。
1.在vps上安装Iperf3
在CentOS 7上使用下列命令即可安装:
yum install -y iperf3在Debian 上使用下列命令安装:
apt install -y iperf32.在pc段下载Iperf3
https://iperf.fr/iperf-download.php#windows
根据自己情况下载对应版本即可
3.在vps上开启Iperf3程序
iperf3 -s -p 52014.在PC端开始测试
首先打开刚才下好的那个Iperf3文件夹,在最上面输入cmd,进入dos窗口。
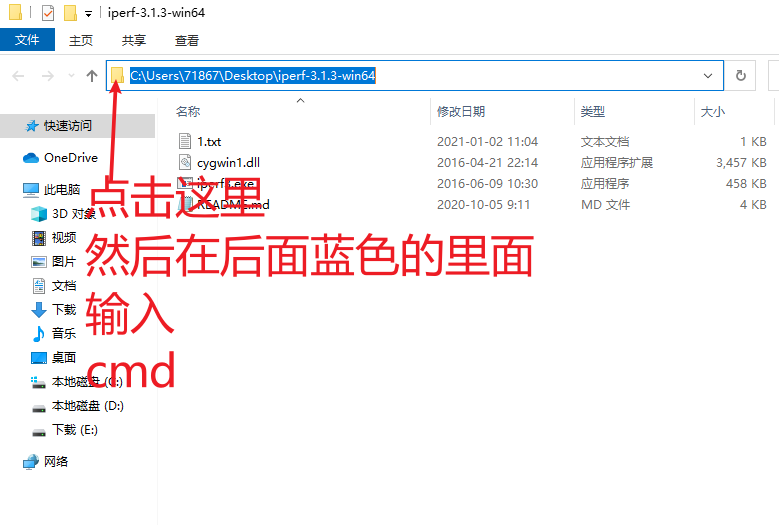
5.输入测速指令
iperf3 -c xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx -P 10 -R -p 5201
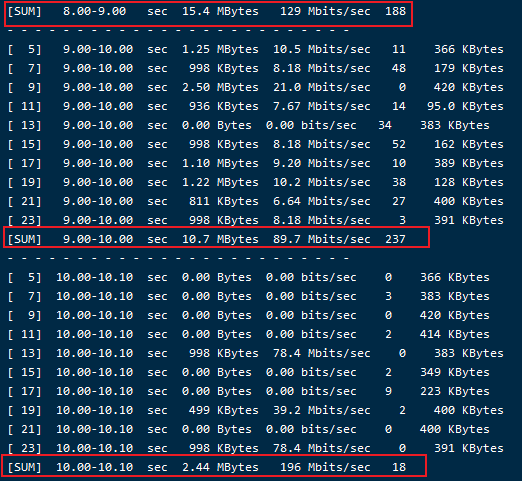
#xxx为你要测试的vps的ip6.如何看测试结果
以上指令为连续10次测速,你只需要看开头为[sum]的数字就行,这个数字是你直接和vps裸连的测试时的数据,不代表你科学上网的速度,也不代表是你和vps永远都是这个速度。
注意:服务器需开放端口5201,测试用的windows测试期间需暂时关闭防火墙,否则会失败。
Usage: iperf3 [-s|-c host] [options]
iperf3 [-h|--help] [-v|--version]
Server or Client:
-p, --port # server port to listen on/connect to
-f, --format [kmgtKMGT] format to report: Kbits, Mbits, Gbits, Tbits
-i, --interval # seconds between periodic throughput reports
-I, --pidfile file write PID file
-F, --file name xmit/recv the specified file
-A, --affinity n/n,m set CPU affinity
-B, --bind <host>[%<dev>] bind to the interface associated with the address <host>
(optional <dev> equivalent to `--bind-dev <dev>`)
--bind-dev <dev> bind to the network interface with SO_BINDTODEVICE
-V, --verbose more detailed output
-J, --json output in JSON format
--logfile f send output to a log file
--forceflush force flushing output at every interval
--timestamps<=format> emit a timestamp at the start of each output line
(optional "=" and format string as per strftime(3))
--rcv-timeout # idle timeout for receiving data (default 120000 ms)
--snd-timeout # timeout for unacknowledged TCP data
(in ms, default is system settings)
-d, --debug[=#] emit debugging output
(optional optional "=" and debug level: 1-4. Default is 4 - all messages)
-v, --version show version information and quit
-h, --help show this message and quit
Server specific:
-s, --server run in server mode
-D, --daemon run the server as a daemon
-1, --one-off handle one client connection then exit
--server-bitrate-limit #[KMG][/#] server's total bit rate limit (default 0 = no limit)
(optional slash and number of secs interval for averaging
total data rate. Default is 5 seconds)
--idle-timeout # restart idle server after # seconds in case it
got stuck (default - no timeout)
--rsa-private-key-path path to the RSA private key used to decrypt
authentication credentials
--authorized-users-path path to the configuration file containing user
credentials
--time-skew-threshold time skew threshold (in seconds) between the server
and client during the authentication process
Client specific:
-c, --client <host>[%<dev>] run in client mode, connecting to <host>
(option <dev> equivalent to `--bind-dev <dev>`)
--sctp use SCTP rather than TCP
-X, --xbind <name> bind SCTP association to links
--nstreams # number of SCTP streams
-u, --udp use UDP rather than TCP
--connect-timeout # timeout for control connection setup (ms)
-b, --bitrate #[KMG][/#] target bitrate in bits/sec (0 for unlimited)
(default 1 Mbit/sec for UDP, unlimited for TCP)
(optional slash and packet count for burst mode)
--pacing-timer #[KMG] set the timing for pacing, in microseconds (default 1000)
--fq-rate #[KMG] enable fair-queuing based socket pacing in
bits/sec (Linux only)
-t, --time # time in seconds to transmit for (default 10 secs)
-n, --bytes #[KMG] number of bytes to transmit (instead of -t)
-k, --blockcount #[KMG] number of blocks (packets) to transmit (instead of -t or -n)
-l, --length #[KMG] length of buffer to read or write
(default 128 KB for TCP, dynamic or 1460 for UDP)
--cport <port> bind to a specific client port (TCP and UDP, default: ephemeral port)
-P, --parallel # number of parallel client streams to run
-R, --reverse run in reverse mode (server sends, client receives)
--bidir run in bidirectional mode.
Client and server send and receive data.
-w, --window #[KMG] set send/receive socket buffer sizes
(indirectly sets TCP window size)
-C, --congestion <algo> set TCP congestion control algorithm (Linux and FreeBSD only)
-M, --set-mss # set TCP/SCTP maximum segment size (MTU - 40 bytes)
-N, --no-delay set TCP/SCTP no delay, disabling Nagle's Algorithm
-4, --version4 only use IPv4
-6, --version6 only use IPv6
-S, --tos N set the IP type of service, 0-255.
The usual prefixes for octal and hex can be used,
i.e. 52, 064 and 0x34 all specify the same value.
--dscp N or --dscp val set the IP dscp value, either 0-63 or symbolic.
Numeric values can be specified in decimal,
octal and hex (see --tos above).
-L, --flowlabel N set the IPv6 flow label (only supported on Linux)
-Z, --zerocopy use a 'zero copy' method of sending data
-O, --omit N perform pre-test for N seconds and omit the pre-test statistics
-T, --title str prefix every output line with this string
--extra-data str data string to include in client and server JSON
--get-server-output get results from server
--udp-counters-64bit use 64-bit counters in UDP test packets
--repeating-payload use repeating pattern in payload, instead of
randomized payload (like in iperf2)
--dont-fragment set IPv4 Don't Fragment flag
--username username for authentication
--rsa-public-key-path path to the RSA public key used to encrypt
authentication credentials
[KMG] indicates options that support a K/M/G suffix for kilo-, mega-, or giga-
iperf3 homepage at: https://software.es.net/iperf/
Report bugs to: https://github.com/esnet/iperf使用方法: iperf3 [-s|-c host] [options] [选项
iperf3 [-h|--help] [-v|--version] [-s|-c host] [options](选项
服务器或客户端:
-p,--port # 要监听/连接的服务器端口
-f, --format [kmgtKMGT] 报告格式: Kbits, Mbits, Gbits, Tbits
-i, --interval # 定期报告吞吐量的间隔秒数
-I, --pidfile 文件 写入 PID 文件
-F、--文件名 xmit/recv 指定的文件
-A,--亲和度 n/n,m 设置 CPU 亲和度
-B,--绑定 <host>[%<dev>] 绑定到与地址 <host> 相关联的接口上
(可选的 <dev> 相当于 `--bind-dev <dev>`)
--bind-dev <dev> 与 SO_BINDTODEVICE 的网络接口绑定
-V, --verbose 更详细的输出
-J, --json 以 JSON 格式输出
--logfile f 发送输出到日志文件
--forceflush 强制每隔一段时间刷新输出
--timestamps<=format>在每行输出的开头发出一个时间戳
(可选“=”和格式字符串,如 strftime(3)
-rcv-timeout # 接收数据的空闲超时(默认为 120000 毫秒)
--snd-timeout # 未确认的 TCP 数据超时
(以毫秒为单位,默认为系统设置)
-d,--debug[=#] 放出调试输出
(可选)可选“=”和调试级别:1-4。默认为 4 - 所有信息
iperf3 主页: https://software.es.net/iperf/
报告错误: https://github.com/esnet/iperf